Health Guide: Top 10 Sources of Omega-3 for a Balanced Diet
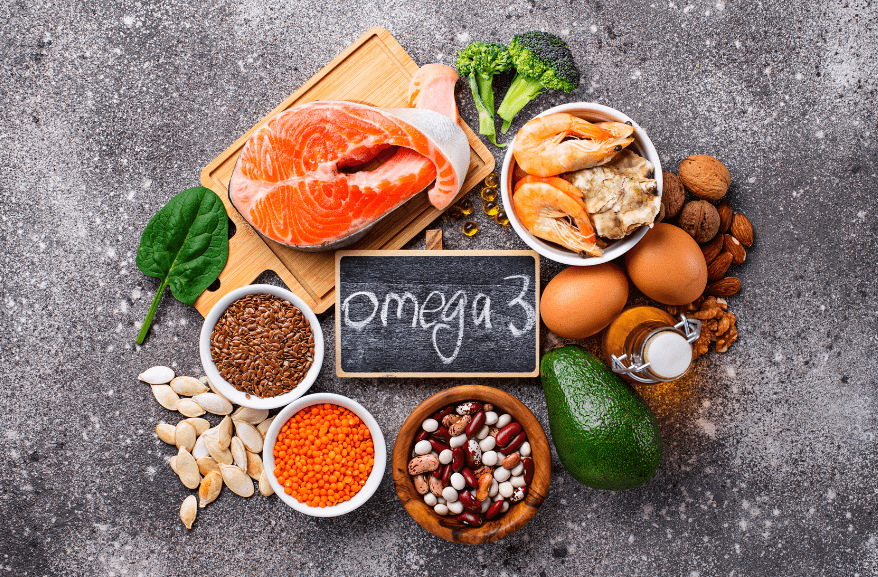
Omega-3 fatty acids have been approved by health experts to be one of the most essential nutrients with miracle health benefits. They are known to play a vital role in ensuring that the cells of our bodies function properly.
Studies suggested a pattern between deficiencies of omega-3 fatty acids and certain chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, inflammation, and brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s.
We have prepared a list of delicious ways to get omega-3 fatty acids into your diet to fill the gaps and increase your ability to dodge such chronic diseases in the long run.
Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Here’s a quick fact: Omega-3s are known to have anti-inflammatory properties and can reduce the risks of heart diseases too. However, it is still not confirmed whether the benefits are the same for consuming supplements, which is why we highly recommend opting for natural omega-3 sources.
Yes, our health comes first, but there’s no reason to think that fighting or preventing our bodies from chronic diseases means eating bland food. Frying fish in a pan or tossing up a delicious salad with excellent sources of omega-3s are great examples of eating consciously.

Health Benefits of Omega-3s
Let’s jump into some of the proven health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids for both physical and mental health.
- Physical Health Benefits
As mentioned earlier, omega-3s are crucial for our bodies’ cell functionality. They enable the formation of molecules called eicosanoids, which have a direct connection with our cardiovascular and immune systems. Moreover, deficiencies in omega-3s may also lead to a clogged and unhealthy pulmonary system, causing lung issues. Doctors have stated that a balanced diet with omega-3s can also improve the condition of the endocrine system, which includes adrenal glands, pancreas, pituitary glands, thyroid glands, and hormones.
- Reduced Inflammations – Researchers confirm that omega-3s can fight inflammation immensely when they compared BMI, body fat, and weight gain among 1053 residents aged over 40 years. Their blood tested positive for CRP (C reactive protein), which is a major triggering factor for inflammation. They were put on a 10-week omega-3-rich diet, which resulted in a significant decline in inflammatory genes.
- Decreased Hunger Levels – 232 candidates suffering from obesity were assessed over a span of eight weeks on a high and low diet of omega-3 fatty acids. The candidates on a high-dose plan reported that their hunger levels were under control, as opposed to the ones who were given lower dosages of omega-3s.
- Improved Blood Sugar – 148 diabetic patients were tested according to an article published in Nutrition, showing improved blood glucose levels with the consumption of omega-3s, leading to reduced risks of diabetes.
- Increased Fat Burn – A study conducted with 75 obese people at the University of South Australia reported significant weight loss (with or without exercise) after incorporating omega-3 into their everyday diet.
- Mental Health Benefits

Omega-3s have also been linked with brain development directly. There was a review released in 2020 stating that 20 percent of our brain’s weight contains omega-3 and omega-6. It was also made clear that mental health conditions like depression, ADHD, and bipolar disorder were triggered by Omega-3 deficiencies. In fact, Alzheimer’s patients are advised to consider Omega-3-rich diets to battle neurodegenerative disorders.
Types of Omega-3s
Omega-3s are a kind of very important fatty acid, and there are three types of them. Let’s break it down for you.
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid)
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid)
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid)
DHA and EPA are known to be found in fish, seafood, krill, algae, and grass-fed beef. Some of the top sources include salmon, tuna, etc.
Whereas ALA exists in plant oils, and our bodies can convert ALA to DHA, the conversion rate is known to be less than 15 percent. This indicates that we need to consume the right amount of Omega-3s that have all three types, for optimal health.
Sources of Omega-3s
Here’s a list of various natural sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
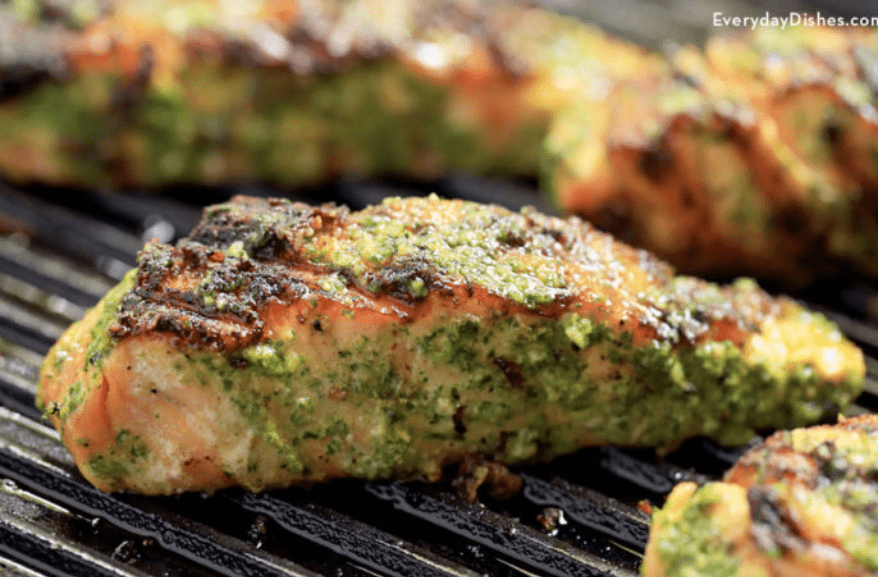
1. Salmon (2,150 mg of EPA and DHA per 100g)
Grilled salmon, anyone?
Salmon has earned the title of being a superfood due to being nutritionally dense in all aspects. It’s packed with protein and various nutrients such as vitamin B, D, and selenium. Fatty fish such as salmon and tuna help to lower the risks of heart issues, dementia, and depression.
2. Mackerel (4,580 mg of EPA AND DHA per 100g)
Another fatty fish, mackerel is small but full of fatty acids, including vitamin B12 and selenium. They are a staple in many nations and super easy to cook. They are usually smoked or grilled, hence requiring almost no preparation.

3. Cod Liver Oil (2,438 mg of EPA and DHA per tablespoon)
Generally considered to be more of a supplement than food, cod liver oil is another great source of Omega-3. Since it is drawn out from the livers of a codfish. It is full of vitamins A and D, and it is advised to consume one tablespoon of cod liver oil daily to meet your daily omega-3 needs.
Please note that consuming more than one tablespoon can be dangerous due to an excess of vitamin A, which can be harmful to your health.
4. Caviar (1,046 mg of EPA and DHA per tablespoon)

Caviar is fish eggs, enriched with omega-3s. They are globally recognized as luxurious and expensive food items, often used in tiny portions for garnishing appetizers.
5. Oysters (391 mg of EPA and DHA per 100g)
Oysters are considered to be one of the most nutritious foods you can eat. They are packed with zinc, copper, and vitamin B12. Oysters are found easily in most parts of the world; in fact, raw oysters are enjoyed as delicacies in some countries.
The best thing about oysters is that they can be eaten as a snack, an appetizer, and even as a meal. Moreover, raw oysters are often consumed as a delicious delicacy in many parts of the world.

6. Herring (2,150 mg of EPA and DHA per 100g)
Herring is a medium-size oily and fatty fish. Usually, it is sold as a canned product, similar to tuna, sardines, etc. It can be eaten pickled, cold, or even stir-fried, depending on your preference. Herring contains selenium and vitamin B12, which meets the daily nutritional requirement of human bodies.
Did you know that it is a common breakfast dish in England, popularly known as kippers, and is served with eggs?
7. Sardines (982 mg of EPA and DHA per 100g)
Another oily and fatty source of omega-3 is sardines, a small fish commonly eaten in many parts of the world as a delicacy, snack, and appetizer. They are high in nutrients with contents of selenium, vitamin D and B12, meeting dietary requirements adequately, if eaten as a whole fish.
8. Anchovies (2,053 mg of EPA and DHA per 100g)
Anchovies are similar to sardines in many ways. They are small and usually packaged in cans or dried. Anchovies are ideally used as a topping on salads, pizzas, or stuffed into capers. They are known to have a strong taste and smell, which is why they are prepared using sauces such as remoulade, Caesar dressing, and Worcestershire sauce.
They are a top source of selenium and niacin, and boned ones contain calcium too.

9. Flaxseed (2,350 mg of ALA per tablespoon)
As the name implies, they are small brown or yellow seeds used to extract oil. They are known to be a superfood due to their high content of omega-3 fat. Flaxseed contains ALA, and omega-3 supplements are made from flaxseed oil.
Flaxseed is an excellent source of various nutrients such as magnesium and fiber. Although they are a better source of omega-6 than omega-3. These small brown or yellow seeds are often ground, milled, or pressed to extract oil.
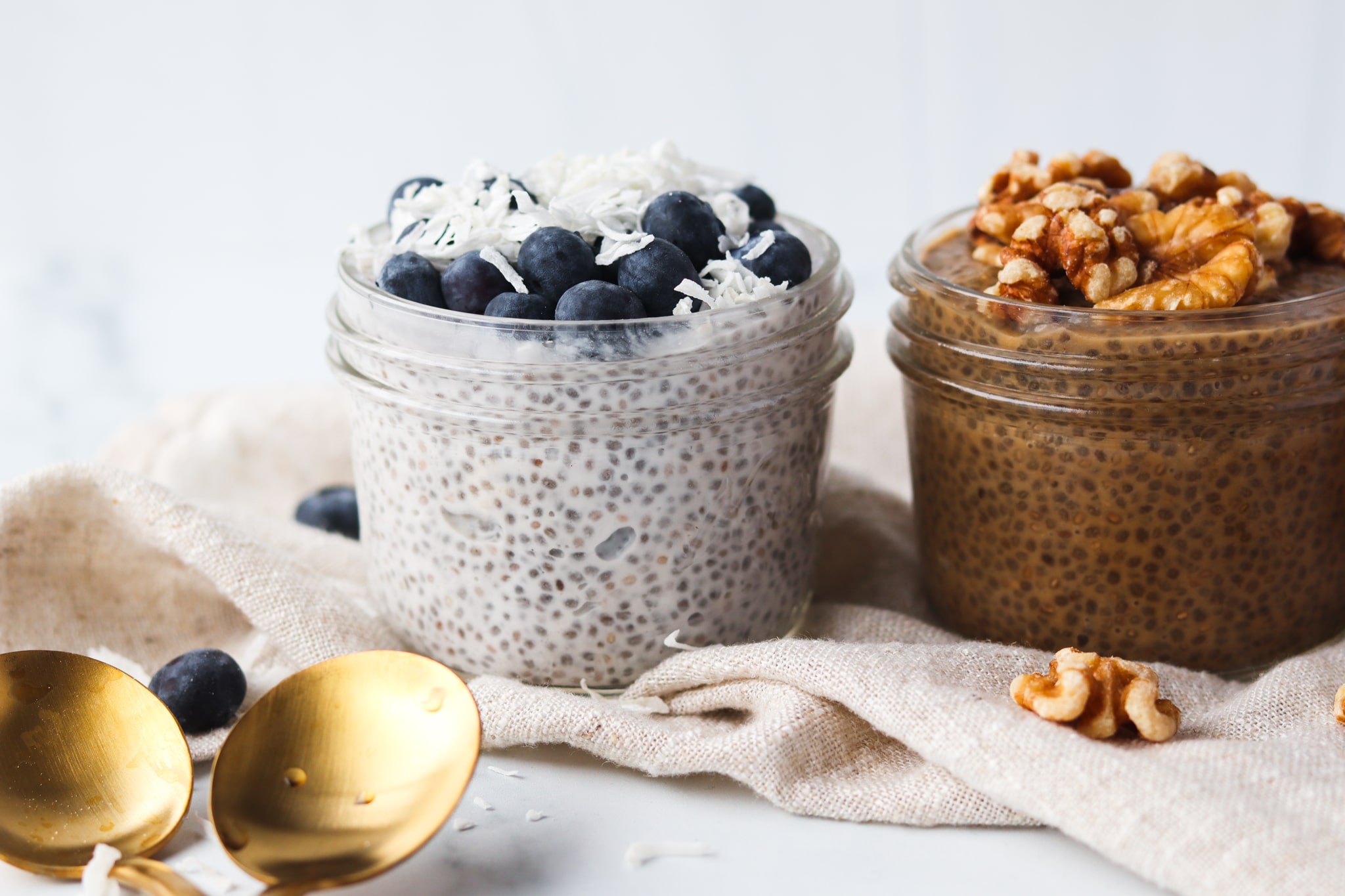
10. Chia seeds (5,050 mg per ounce, 28g)
Chia seeds, yet another superfood, are known to be extremely rich in nutrients containing protein, selenium, magnesium, amino acids, and many other nutrients. The nutrition source suggested that 60 percent of the oil in chia seeds has omega-3 fatty acids, benefiting and reducing the risks of cardiovascular diseases. It is known to keep blood pressure under control, regulate heartbeats, and ward off blood clots.
Chia seeds are also prescribed to people suffering from high levels of cholesterol, as it helps lower LDL cholesterol.
Chia seeds can be eaten in many different ways. The simplest way is to soak it in warm water for 15 minutes before drinking it. If you want to have a bit of fun with it, you can look up chia seed pudding recipes too.
Conclusion
Lastly, don’t limit yourself to this list of delicious ways to get omega-3s. It’s important to know that there are other sources of omega-3 fatty acids such as tuna, walnuts, soybeans, wild rice, grass-fed beef, spinach, and many more.
All these whole foods contain an adequate amount of omega-3s to meet your dietary requirements and live a healthy life, both physically and mentally.
However, if you feel that incorporating these food items into your diet is not ideal, you should speak to your doctor for alternatives such as supplements.





